Prostatitis in men is the most common urological disease in men. According to statistics, the number of men with this diagnosis is up to 8% of the male population of the world, of which 1/3 are owners of the chronic form of the disease. In 40% of cases, chronic prostatitis in men is detected before the age of 40.
A distinctive feature of prostatitis is that its acute form is almost completely absent. As soon as it appears, it immediately acquires a chronic form.
Cases of complete recovery (spontaneous or as a result of treatment) after the initial acute stage are fewer. The course of the disease is very slow, and the symptoms of prostatitis often subside. Prostatitis manifests itself in three main syndromes: painful, sexual, and dysuric.
Causes of prostatitis in men.
The causes of prostatitis are infections, stagnation of the prostate gland, and a combination of these two factors. One of the predisposing factors for the development of chronic prostatitis is also the presence of benign hyperplasia in the patient.
The infection can enter the prostate gland by:
- through the urethra by sexual contact, as a complication after infectious urethritis;
- through the blood of existing infections in the body (decayed teeth, sinusitis, pneumonia and others);
- through the lymph of inflamed internal organs (intestinal dysbiosis, hemorrhoids, inflammation of the rectum).
Most often, prostatitis in men is non-infectious in nature (bacterial prostatitis). Its main reason is a violation of blood circulation in the prostate and surrounding organs as a result of stagnation of secretions in it.
In the prostate gland, stagnation of secretion can occur due to the following factors:
- prolonged sexual abstinence;
- unrealized sexual contact after sexual arousal;
- interrupted sexual intercourse;
- faulty ejaculation.
Factors that predispose to the development of prostatitis:
- irregular sex life;
- hypothermia;
- hypodynamics;
- Chronic stress;
- chronic alcoholism and others.
Symptoms of prostatitis in men.
- pain in the genital area;
- pain in the groin, perineum, suprapubic region;
- frequent need to urinate;
- painful sensations when urinating;
- pain with ejaculation;
- defective erection or lack thereof.
Most often, chronic prostatitis is predisposed to neurasthenia caused by the above disorders.
Pain in prostatitis, as a rule, is radiant in nature, that is, it radiates to the sacrum, perineum or scrotum. From the prostate there are nerve endings to all the organs of the small pelvis, so pain is often transmitted to the lower back. Its intensity is different, from subtle to pronounced, which even interrupts sleep. The pain can intensify, weaken with sexual abstinence or, conversely, occur with excessive sexual activity or ejaculation. It should be noted that pain in the sacrum does not always indicate prostatitis; they can also indicate osteochondrosis.
How prostatitis manifests itself in men chronically, here the situation is completely different. Its course is undulating; periodic exacerbations are replaced by more or less prolonged remissions, during which the disease does not manifest itself in any way. In this case, men rarely go to the doctor and prefer to sit at home. However, this is not a way out of the situation, since prostatitis in men, its exacerbation, will progress over time. And, spreading through the genitourinary system, it will lead to cystitis and pyelonephritis.
Prostatitis in men: consequences
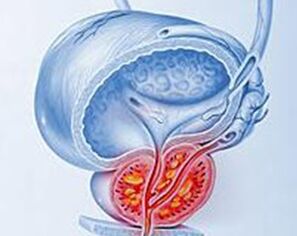
As a general rule, patients with acute prostatitis seek medical help in a timely manner. But if you do not go to a urologist in time, there is a high probability of focal purulent inflammation - an abscess of the prostate gland. In this case, the body temperature can rise to 39-40 ° C, it becomes frantic (the drop in body temperature exceeds 1 ° C), and the intense fever is periodically replaced by chills. The pain in the perineum is so pronounced that urination and defecation become extremely impossible. Gradually, the prostate gland swells, and as a result, urinary retention occurs. Fortunately for the men themselves, they rarely reach that state.
Vesiculitis is one of the most common complications of prostatitis, when the seminal vesicles become inflamed. And also epididymoorchitis, characterized by inflammation of the testicles and their appendages. Treatment of chronic prostatitis in men caused by these diseases will be extremely difficult and time consuming.
Both diseases can lead to infertility. Everything described is more related to chronic prostatitis, which has a specific etiology and which has developed as a consequence of sexually transmitted diseases. A urologist prescribes how to treat prostatitis in men and drug treatment in any form.
Treatment of prostatitis in men.
How to treat prostatitis in men depends on the form of the disease and its appearance. In the treatment of acute prostatitis, antibiotics are used that penetrate well into the tissue of the prostate gland. The prescribing specialist must take into account all the individual characteristics of the disease, the state of the body's immune system and the presence of infectious agents. If the course of the disease is not complicated by anything, then patients with acute prostatitis are treated only on an outpatient basis. Only patients with signs of severe and severe poisoning are subject to hospitalization. Such physiotherapeutic methods are widely used: magnetic laser induction therapy, reflexology, ultrasound, treatment of prostatitis with leeches. A good effect can be achieved by using herbal preparations (herbal medicine), enzymes, cytomediators, immunomodulators. Surgery for prostatitis is indicated in the following cases:
- a prostate abscess (transurethral or transrectal drainage of the abscess);
- acute urinary retention (puncture epicistostomy).
Treatment of chronic prostatitis in men is done on an outpatient basis, but for a longer period. In addition to the use of antibiotics, suppositories, and heat treatments, prostate massages and reflexology are also performed. Also, patients with prostatitis are advised to have an active lifestyle and the exclusion of alcoholic beverages and spicy foods from use.
Prevention of prostatitis in men.
Timely treatment of prostatitis in men, as well as its prevention, contributes to a speedy recovery. As a preventive measure to prevent the development of chronic prostatitis, it is recommended:
- regular sex life;
- properly selected diet (varied and nutritious foods with the exception of spicy and irritating foods);
- no alcohol abuse;
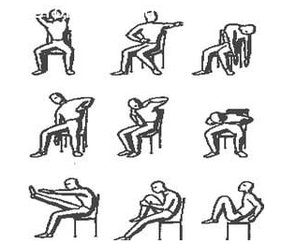
- moderate physical activity aimed at improving blood circulation in the organs of the genitourinary system and strengthening the muscles, Kegel exercises (tension of the muscles of the perineum with retraction of the anus);
- adequate and timely treatment of infectious diseases of other organs;
- prevention of stagnation in the small pelvis by means of physiotherapy methods.
To exclude recurrence of the disease: secondary prevention of prostatitis, which includes primary prevention and:
- regular preventive exams with a urologist;
- pass preventive courses of treatment with fortifying methods, multivitamins;
- physiotherapy methods (especially in the spring and autumn periods).